The modern digital market does not forgive technical errors, and competition in app stores is fiercer than ever. For software houses and professional technology companies, a mobile application is not just an attractive interface, but primarily a complex, multi-layered backend and frontend architecture that must operate flawlessly 24/7. In a dynamic environment where the tech stack changes every quarter, the road from an empty code repository to a stable production build in the App Store or Google Play is full of hidden traps. Technical success is the result of systematic elimination of technical debt and precise system architecture planning from the very first sprint. How to effectively design scalable solutions, avoid critical performance issues (such as memory leaks or UI thread blocking), and ensure mobile app security according to OWASP Mobile Top 10 standards? In this technical guide, we will deeply analyze the critical engineering aspects of the mobile app development process.
Mobile App Development Process: How to Design During Development?
A professional mobile app development process goes far beyond just writing source code. The key engineering challenge is designing and implementing an efficient CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) pipeline that fully automates the processes of building, testing, and deploying new versions. Tools such as Bitrise, Jenkins, or GitHub Actions become essential to maintain a high pace of work while preserving quality. A common mistake made by development teams is the lack of automated regression tests, which inevitably leads to errors appearing in the production environment after every deployment. To ensure stable and predictable app performance, it is necessary to use proven architectural patterns such as MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel), VIPER, or Clean Architecture. They allow for the separation of business logic layers from the presentation layer, which significantly facilitates later code maintenance and testability (unit testing).
In the development process, the Discovery phase and the conscious selection of the appropriate tech stack are absolutely critical. A deep understanding of the technical user needs – for example, the necessity of offline operation (offline-first approach), advanced background data synchronization, or handling push notifications in real-time – determines the choice of local database (Realm, CoreData, Room) and communication protocols (REST vs GraphQL vs WebSocket). Ignoring API technical specifications or lacking contracts (e.g., Swagger/OpenAPI) at an early stage is a simple recipe for costly refactoring in the future. Even the best-optimized client code will not fix errors in the backend business logic or performance issues with SQL queries. Therefore, the cost of creating an app grows exponentially with every late detection of architectural errors that could have been avoided at the system design stage.
If you want to delve into the stages of product creation from a business and strategic perspective, check out our article on mobile app development from idea to implementation – a complete guide.
Choosing Mobile Technologies: Multi-platform App Development vs Native
The strategic decision regarding the choice of mobile technologies is always a compromise between maximum performance and cost optimization through code sharing. Fully native solutions (iOS/Swift, Android/Kotlin) give programmers direct, low-level access to system APIs and guarantee the highest possible graphics rendering performance, which is crucial in games or AR applications. On the other hand, hybrid apps and modern cross-platform frameworks, such as Flutter or React Native, although significantly speeding up app development thanks to features like Hot Reload, can generate problems with the so-called “bridge” during intensive communication with native device modules. One should not fear the topic of multi-platform apps, but engineers must be aware of the overhead on the installation package size (APK/IPA) and potential frame drops.
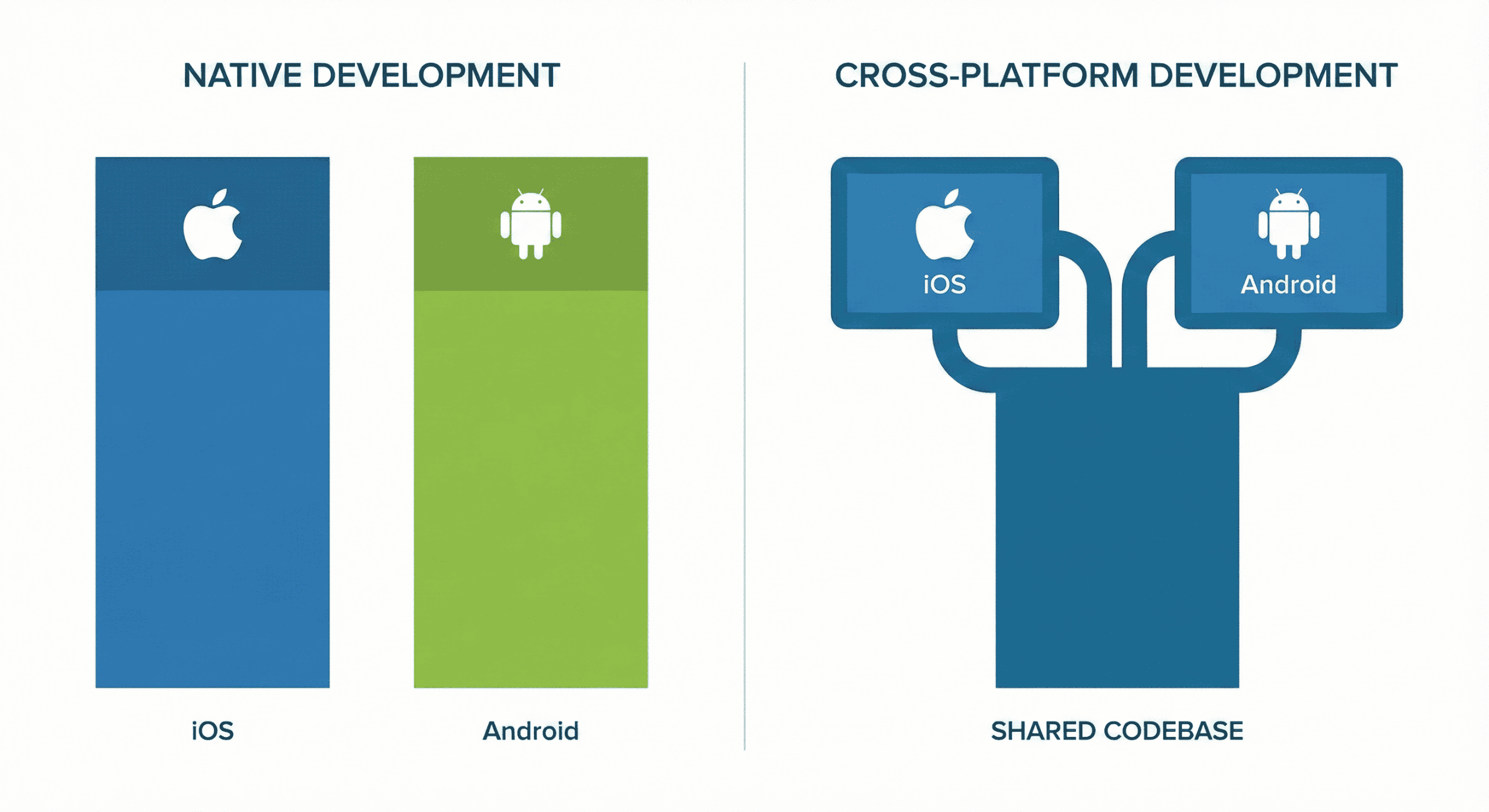
The final choice depends on specific business and technical requirements. Applications requiring intensive calculations, real-time image processing, or the use of ARKit/ARCore are definitely better designed natively. In the case of apps that are typically CRUD, forms, or e-commerce, the cross-platform approach allows saving up to 40% of time, enabling the simultaneous release of the app to the market on both leading platforms. However, the key to success is skillful management of the application lifecycle and state (State Management – e.g., BLoC, Redux, MobX), regardless of the adopted app development approach.
iOS and App Store: Managing App Distribution in Stores
The Apple ecosystem is a real challenge for DevOps engineers and Release Managers. Creating an iOS app is inextricably linked with the complicated and often frustrating process of Code Signing. Problems with developer and distribution certificates, expiring Provisioning Profiles, or incorrect configuration of Entitlements files (e.g., for Apple Pay or Push Notifications) are daily bread in iOS projects. The end user does not see this, but even the smallest error at this stage completely prevents distribution or build installation. Furthermore, the user interface must strictly comply with the restrictive Human Interface Guidelines, which often forces programmers to implement native UI components instead of custom solutions that could disrupt the experience (UX).
Publication in the App Store and the presence of the app in stores is often a battle with Rejections during the Review process. Apple rigorously verifies compliance with Guideline 4.0 (Design) or 2.1 (Performance). A common reason for rejection is the use of private APIs, lack of full IPv6 support in cellular networks, or unclear messages when requesting data permissions (camera, location, contacts). Every subsequent update must go through the same verification process. If the app crashes on launch or violates privacy rules, it will be immediately blocked. Effective management of this process and automation of build dispatch to TestFlight (e.g., using the fastlane tool) is absolutely essential here.
Android and Google Play: App Performance and Fragmentation
The Android system presents developers with unique challenges related to huge hardware and software fragmentation (different API Levels). Your product must work correctly on thousands of hardware combinations – from flagships to budget phones. Every smartphone has a different screen DPI, which forces the creation of flexible layouts (ConstraintLayout) and the preparation of graphic resources in many densities. App design must also take into account various, often non-standard implementations of the system WebView by system overlay manufacturers. An important aspect is also the optimization of project build time – the Gradle build system can be slow with large projects, requiring configuration tuning and modularization.
A critical technical problem, monitored by Google Play, is the ANR (Application Not Responding) error. It appears when the app operation blocks the main UI Thread for too long (usually over 5 seconds). It is necessary to rigorously move all I/O operations, network queries, and heavy calculations to background threads (using Kotlin Coroutines or RxJava). Additionally, system energy-saving mechanisms (Doze Mode) can aggressively “kill” background processes. Positioning algorithms promote apps with a low failure rate (Crash Rate) and ANR, monitored by the Android Vitals console.
Effective mobile app development requires testing on physical device farms (Device Farms, e.g., Firebase Test Lab) to catch specific errors. The app must also be perfectly optimized for RAM usage to avoid being killed by the system’s Low Memory Killer (LMK), which is extremely frustrating for the user.
Mobile App Security and Aspects of App Security
In a technical context, mobile app security is a constant battle against Reverse Engineering and network attacks. By definition, a mobile app operates in an untrusted environment and should not trust data coming from the server or the system on which it is running (especially on rooted devices). In the era of GDPR and PSD2 directives, app security issues require the implementation of specific, advanced protective mechanisms.
The absolute basis is SSL/TLS Pinning, which prevents Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks, making it impossible for an attacker to swap the server certificate and eavesdrop on the transmission. Production code should always undergo obfuscation and minification processes (e.g., using ProGuard or R8 on Android) to maximally hinder decompilation and analysis of business logic by third parties. Implementation of the OAuth2 authorization standard and secure token management (Refresh Token Rotation) is a necessity. In the case of apps requiring the highest security (FinTech sector, banking), RASP (Runtime Application Self-Protection) systems and secure hardware key storage are used. Remember that hardcoding API keys is a critical app security error.
Mobile App Testing, Testing, and App Performance
Performance in mobile is not just a subjective feeling; these are hard, measurable metrics: app start time (Cold Start vs Warm Start), CPU usage, RAM allocation, and frame rate stability. If the app “drops frames” (Jank) while scrolling a list, mobile app testing must include deep profiling. Tools such as Android Profiler or Xcode Instruments allow detecting subtle memory leaks, which over time inevitably lead to OOM (Out Of Memory) crashes.
App performance also depends directly on the optimization of network queries and effective data caching. The testing process should cover the testing pyramid: unit tests for business logic, integration tests, and automated app testing in the UI layer (Espresso, XCUITest). It is also worth regularly checking the app for behavior under weak or unstable internet connection. Good and stable app operation is also verified on various physical devices.
Further App Development and Updates in the Development Process
Releasing the first version of the app (MVP) is just the beginning of a never-ending battle with technical debt. The dynamic market forces continuous dependency management, which often introduces “breaking changes”. Essential is further app development based on hard data from error reports. Technologies evolve at a breakneck pace – migration from Java to Kotlin or from Objective-C to Swift are multi-year processes, but necessary.
Regular updates ensure compatibility with new versions of operating systems. Modern apps must be built in a modular way to facilitate team scaling and adding new features without the risk of regression in old modules. In the development process, it is worth factoring in time for refactoring and care for code quality (Clean Code, SOLID), which is the foundation of long-term maintenance.
Summary: Key to Success and App Success
Achieving market app success today requires engineering perfection. The key to success lies in a stable, scalable backend, perfectly optimized frontend, and secure, encrypted communication.
In summary, mobile app development involves solving specific, difficult technical problems daily: from complicated Gradle/CocoaPods configuration, through fighting Android fragmentation, to meeting the strict guidelines of Apple and Google stores. However, a well-written, modern app that is technically polished, intuitive, and secure will always defend itself in the market. Remember the technical priorities:
- Implement multi-layered mobile app security (SSL Pinning, database encryption, RASP).
- Test the app automatically and manually on physical devices (Device Farm), not just on emulators.
- Continuously monitor ANR indicators, Cold Start Time, and Crash-free users, reacting to anomalies.
- Plan mobile app development in the roadmap, allowing time for regular repayment of technical debt and refactoring.
If your app meets these rigorous technical standards and is free of critical errors, you have a real chance for business success. Regardless of whether you publish in the App Store or Google Play, code and architecture quality always translates into end-user satisfaction and loyalty.
Looking for a platform tailored to your needs?
Contact us via the contact form, and we will tell you the details!